Log Alchemy: Meaningful Kubernetes Logs with Seq and Fluent Bit
Table of Contents
Let’s progress from checking Kubernetes logs in a terminal to using structured log data for searching, visualising and setting alerts within a web based user interface. We will use our Nginx deployment to demonstrate.
Structured logging involves defining shapes for log data, most often represented in JSON using key value pairs.
As compared to unstructured text log entries, structured logs make it easier to find events and turn log data into insights. Think using query languages on log entries instead of grep in a terminal.
With structured log data and a platform for consuming that data, we can:
- search
- filter
- visualise
- aggregate, and
- set alerts.
What is Seq?#
In their own words, Seq is a self-hosted search, analysis and alerting server for structured log data.
It consumes log data sent to it and allows querying that data using an SQL like language. Queries can be turned into graphs and added to dashboards. Alert plugins can be setup to send notifications to Slack, Teams, email, and many other communication channels.
In the context of Kubernetes and this example site, we can use Seq to monitor:
- application data, e.g.
- Nginx traffic
- Vault status
- nodes
- containers, and
- control planes.
Note, Seq is not open-source and requires a subscription when the UI is used by more than one person. This business model works well enough for us as it enables homelabs to use it and devs to play around to see how it compares with other tools filling the same niche.
For an open-source alternative, checkout Elasticsearch has the largest market share at time of writing. Elasticsearch has many other functions and a bit of a steeper learning curve as a result.
What is Fluent Bit?#
Fluent Bit reads and parses log files and then sends the data to a specified destination using one or more of many available protocols. Familiar with Logstash? Fluent Bit does a similar job.
Fluent Bit can be deployed to Kubernetes as a DaemonSet and then individual parsers may be specified on a deployment or pod basis using annotations. A DaemonSet being a Kubernetes resource which ensures a pod is running on each node in the cluster.
Example#
Checkout the end result in GitHub
Tech Stack#
- Ubuntu Linux 22.04
- K3s (Kubernetes) 1.28.5
- Fluent Bit 2.2.2
- Seq 2024.1
- Helm 3.14.0
- Nginx 1.25.3
Bring Your Own#
- Host running Ubuntu Linux
- Kubernetes
- Helm
- Nginx
- Email account with SMTP
- To send alerts
Steps#
Setup and Install Seq with Helm#
Configure Seq’s Helm Values File#
Add contents to file deploy/helm/seq-values.yaml
# https://github.com/datalust/helm.datalust.co/blob/main/charts/seq/values.yaml
# Accept events in the GELF format and forward them to Seq
gelf:
enabled: true
## Configure probe values
livenessProbe:
enabled: true
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 0
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
readinessProbe:
enabled: true
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 0
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
startupProbe:
enabled: true
failureThreshold: 30
periodSeconds: 10
By default, Seq will provision a 8GB PersistentVolumeClaim using the default provider for storing log data.
See their values.yaml example file for further details.
Define a Service for Seq#
To allow us to access Seq’s UI via an exposed port on the node.
Add contents to file deploy/seq-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: seq-service
name: seq
spec:
ports:
- name: seq-ui
port: 8000
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: seq
type: LoadBalancer
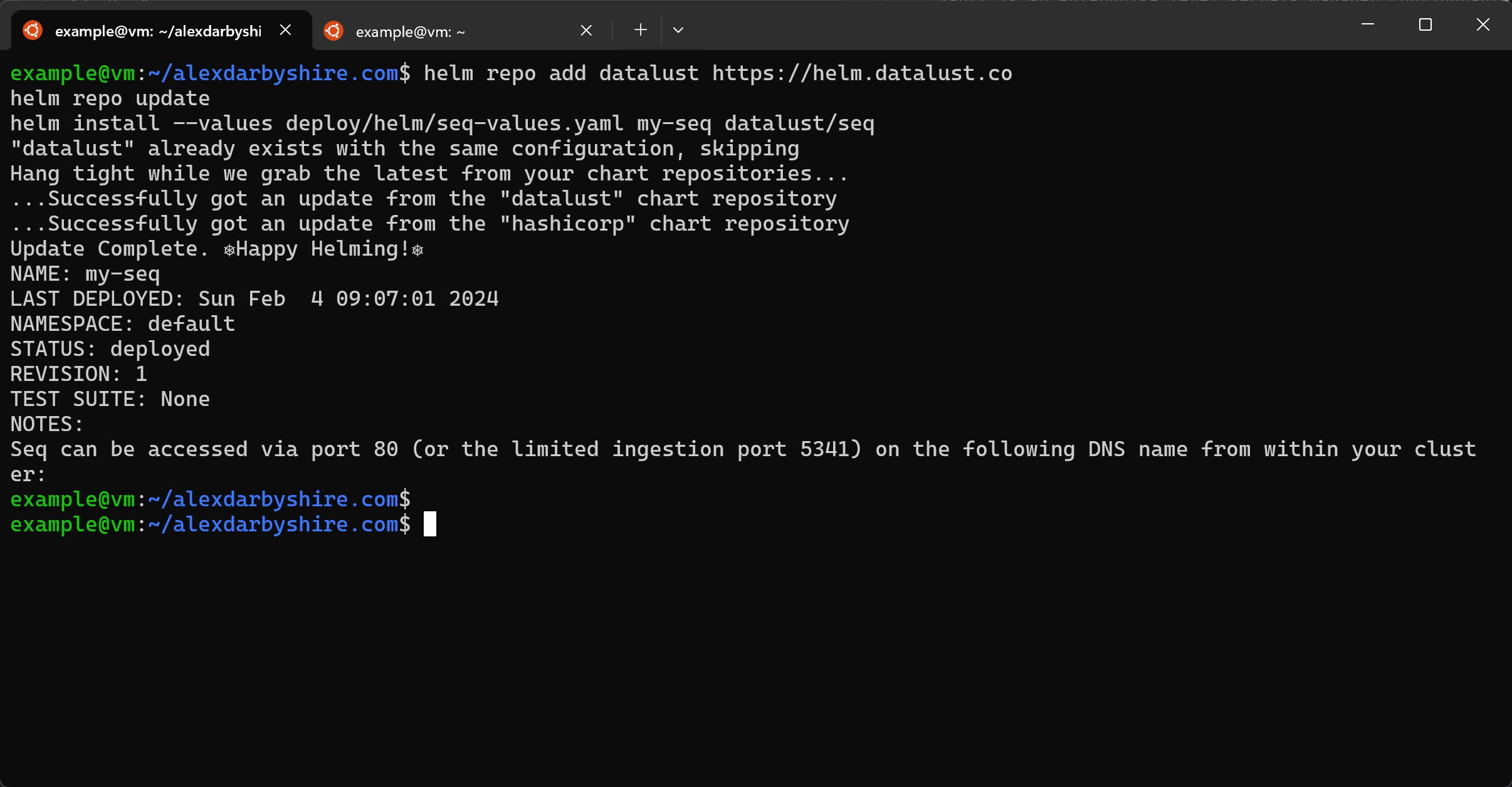
Install Seq using Helm#
helm repo add datalust https://helm.datalust.co
helm repo update
helm install --values deploy/helm/seq-values.yaml my-seq datalust/seq
Add Seq Kubernetes Service#
kubectl apply -f deploy/seq-service.yaml
Setup and Install Fluent Bit as DaemonSet with Helm#
Configure Fluent Bit’s Helm Values File#
Add contents to file deploy/helm/fluent-bit-values.yaml
Notably, we configure GELF Output, a custom Nginx parser, add Seq’s internal cluster hostname and disable Keep_Log Off wtihin the kubernetes filter.
How to set up a Fluent Bit Regex Nginx parser to capture IP for proxied requests#
We create a custom parser to pick up the http_x_forwarded_for IP which Fluent Bit’s baked Nginx parser does not include.
Note, this parser is included in the fluent-bit-values.yaml file linked above.
A custom parser is required in our setup as the remote IP will always be our Cloudflared pod which is forwarding requests received at the other end of the tunnel.
The parser uses a Regular Expression and looks like this:
[PARSER]
Name nginx-with-forwarded-for
Format regex
Regex ^(?<remote>[^ ]*) (?<host>[^ ]*) (?<user>[^ ]*) \[(?<time>[^\]]*)\] "(?<method>\S+)(?: +(?<path>[^\"]*?)(?: +\S*)?)?" (?<code>[^ ]*) (?<size>[^ ]*)(?: "(?<referer>[^\"]*)" "(?<agent>[^\"]*)") "(?<http_x_forwarded_for>[^ ]*)"$
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
Were we not using Helm to deploy, it would be added to a Kubernetes ConfigMap (which Helm does under the hood).
The parser relies on Nginx using its default ‘out-of-the-box’ log format which is defined within one of the Nginx image’s internal conf files, /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. Here is an excerpt for reference:
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
This could be approached a different way by configuring Nginx to log in structured manner in the first place by outputting JSON. This would reduce compute requirements in terms of Fluent Bit not needing to apply Regex.
Install Fluent Bit using Helm#
helm repo add fluent https://fluent.github.io/helm-charts
helm upgrade --install --values deploy/helm/fluent-bit-values.yaml fluent-bit fluent/fluent-bit
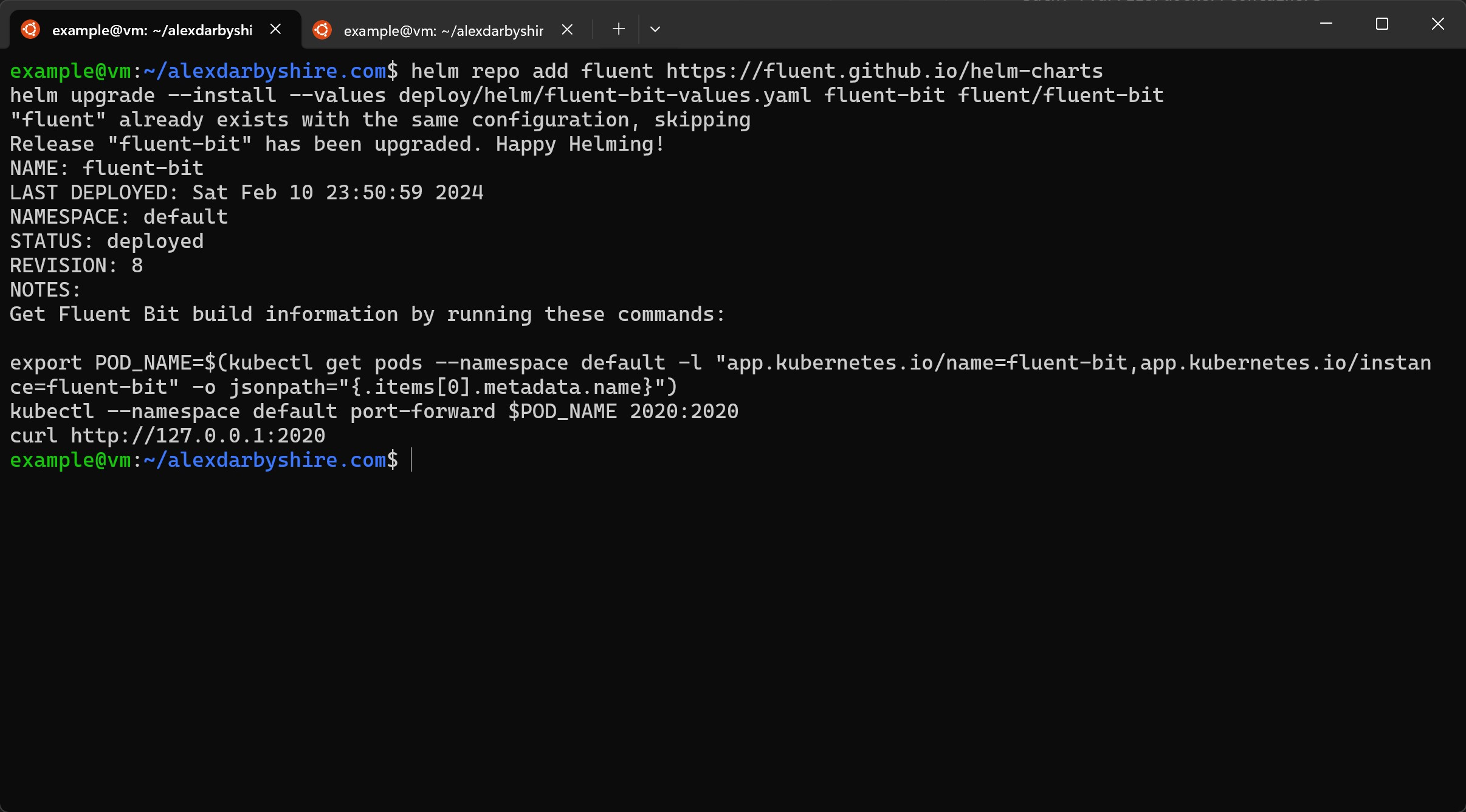
Screenshot above shows output when Fluent Bit was already installed, it is very similar to the fresh install’s output and the commands used remain the same
Update Nginx Deployment Manifest to use Custom Fluent Bit Parser#
To do this, we add an annotation to our Nginx’s deployments pod template which is in deploy/hugo-cloudflared.yaml
73apiVersion: apps/v1
74kind: Deployment
75metadata:
76 labels:
77 app: nginx-hugo
78 name: nginx-hugo-deployment
79spec:
80 replicas: 1
81 selector:
82 matchLabels:
83 app: nginx-hugo
84 template:
85 metadata:
86 labels:
87 app: nginx-hugo
88 annotations:
89 fluentbit.io/parser: nginx-with-forwarded-for
90 spec:
91 containers:
92 - image: localhost:5000/alexdarbyshire-site:latest
93 name: nginx-hugo
94 ports:
95 - containerPort: 80
96 restartPolicy: Always
Apply Changes to Nginx Deployment#
kubectl apply -f deploy/hugo-cloudflared.yaml
Add Dashboard for Nginx to Seq#
Add New Dashboard#
Click the little plus with circle around it symbol.
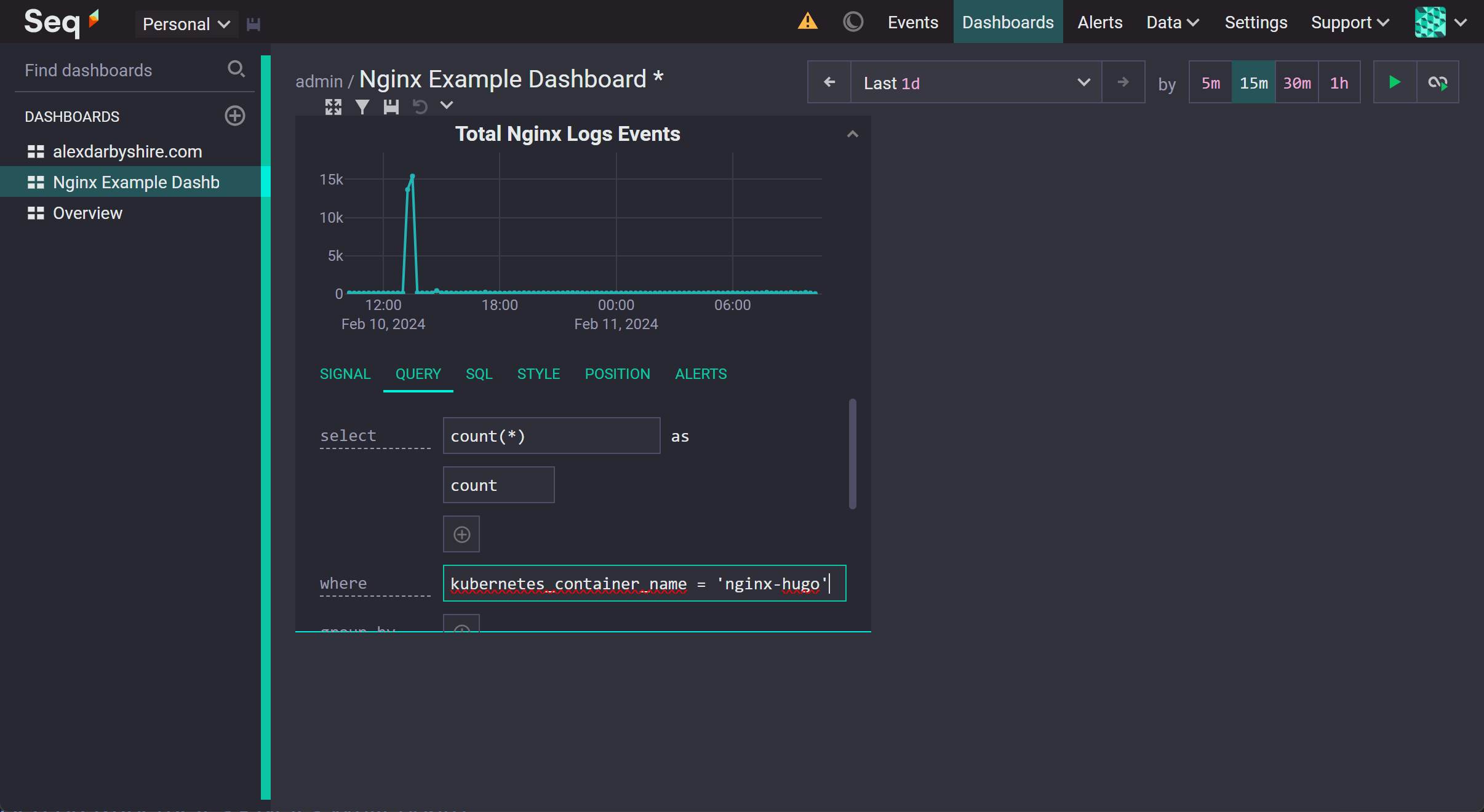
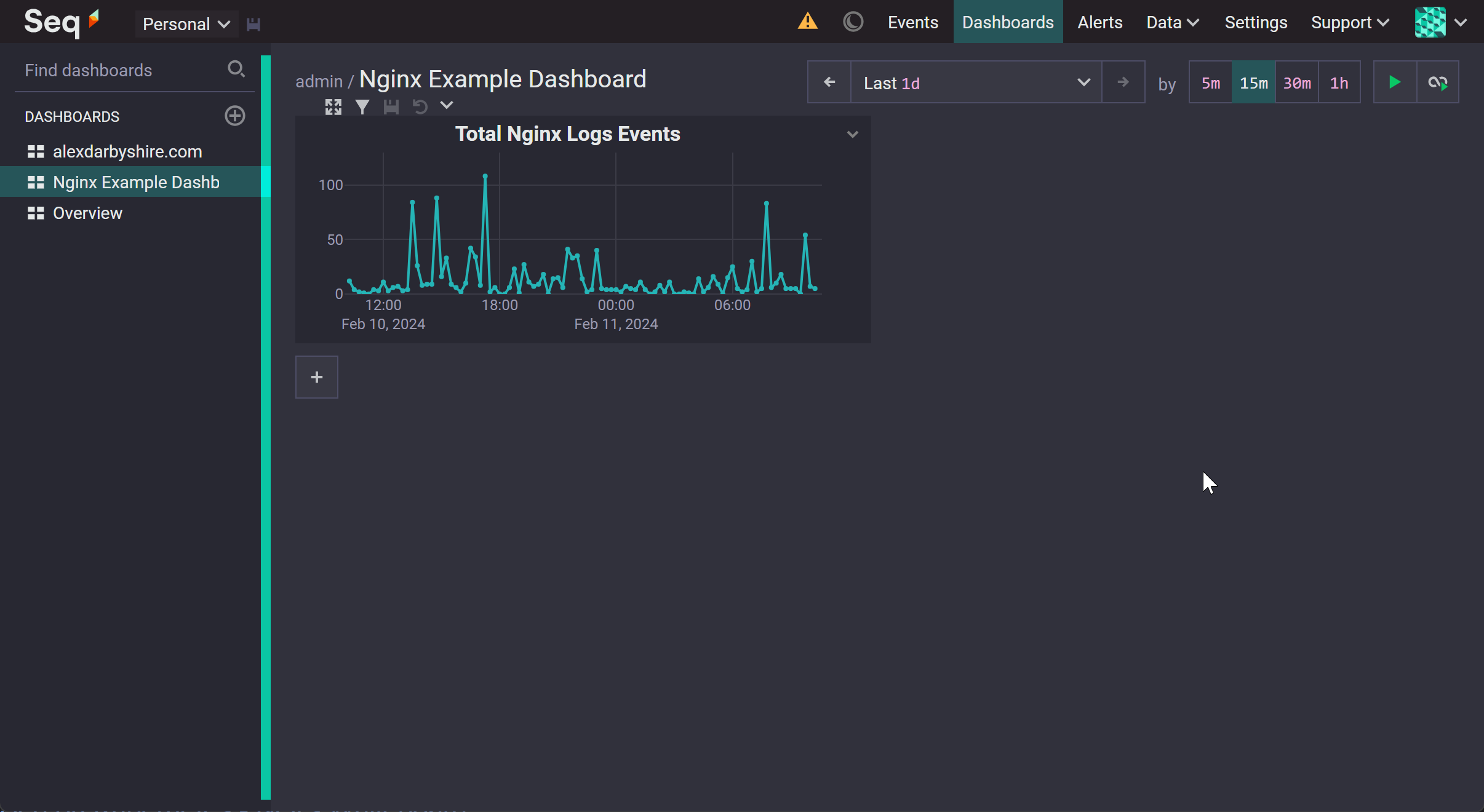
Create a Graph of Total Nginx log events#
Click the plus to add a new visualisation, click query and then add a where clause kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo', add a title e.g. Total Nginx Log Events.
Then click the save icon (little digital floppy disk looking thing to the left of the filter icon).
Other Dashboard Query Examples#
Here we will run through the queries used to create these visualisations in this dashboard using Seq’s query language.
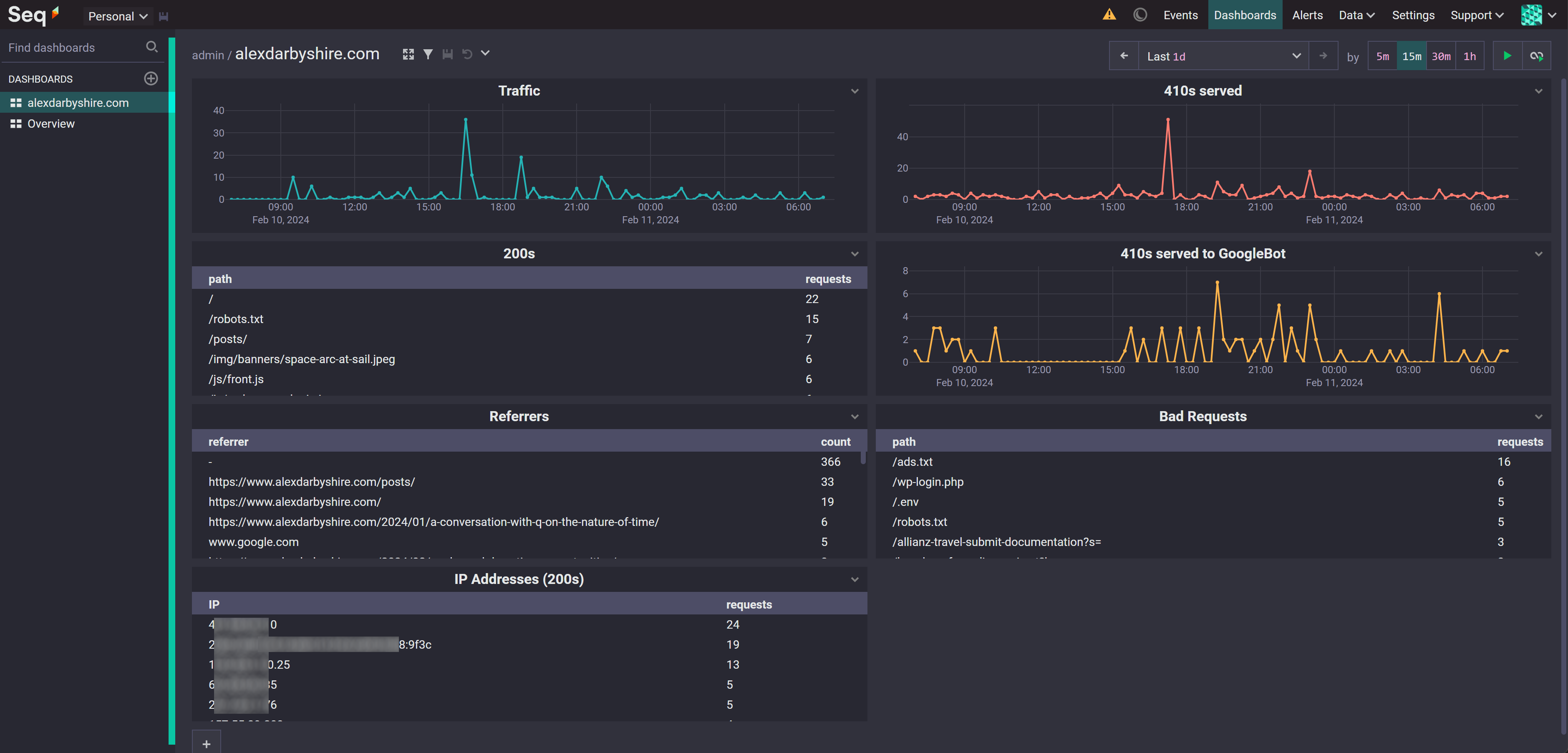
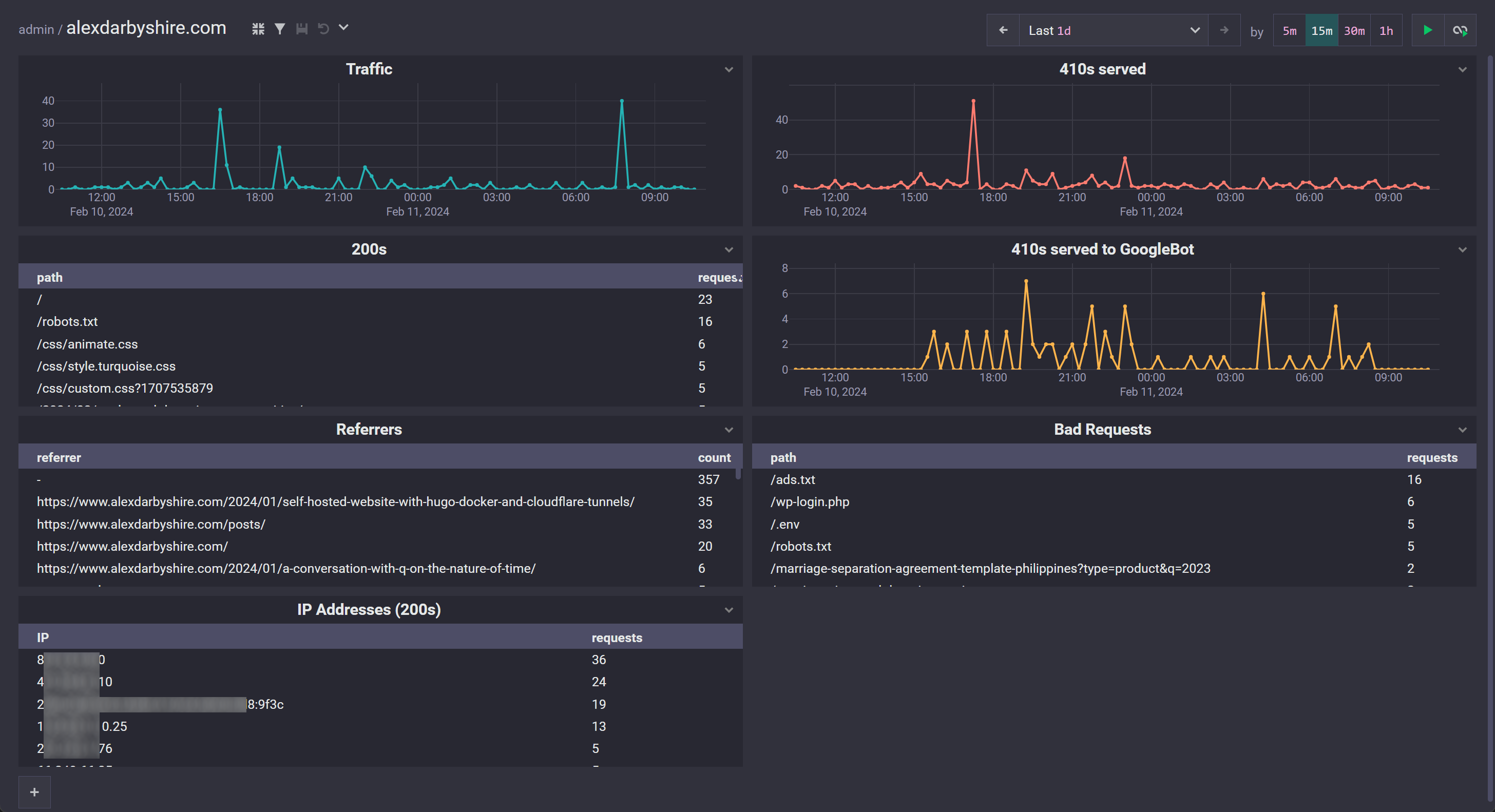 Note, in typical circumstances the 410s (Gone) here would be 404s (Not Found). Something funky happened to my domain while it was dormant, possibly the Namecheap hosting IP I previously used was re-assigned, and GoogleBot indexed ~4000 spammy links. For a little while I am returning 410s for every bad link requested.
Note, in typical circumstances the 410s (Gone) here would be 404s (Not Found). Something funky happened to my domain while it was dormant, possibly the Namecheap hosting IP I previously used was re-assigned, and GoogleBot indexed ~4000 spammy links. For a little while I am returning 410s for every bad link requested.
Traffic#
Query
select count(*)
as count
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR-OWN-IP-HERE' and code <> '410'
200s#
HTTP responses with status code 200 aggregated by path.
Query
select count(*) as
requests
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR-OWN-IP-HERE' and code = '200'
Style
Type Table
Referrers#
Count of HTTP Referrer aggregated by referrer.
Query
select count(referer)
as count
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR-OWN-IP-HERE'
group by referer as referrer
order by count DESC
limit 100
Style
Type Table
IP Addresses (200s)#
Count of 200 requests aggregated by IP address.
Query
select count(http_x_forwarded_for)
as requests
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR-OWN-IP-HERE' and code = '200'
group by http_x_forwarded_for as IP
order by requests DESC
limit 100
Style
Type Table
410s served#
Count of responses with HTTP 410 status code.
Query
select count(*)
as count
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR_OWN_IP_HERE' and code = '410'
Style
Palette Red
410s served to GoogleBot#
Count of responses to GoogleBot with HTTP 410 Status code.
Query
select count(*)
as count
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR_OWN_IP_HERE' and code = '410' and agent like '%Googlebot%'
Style
Palette Orange-purple
Bad Requests#
Count of responses with status code other than 200 aggregated by requested path.
Query
select count(*)
as requests
where kubernetes_container_name = 'nginx-hugo' and http_x_forwarded_for <> 'YOUR_OWN_IP_HERE' and code <> '200'
group by path
order by requests DESC
limit 100
Style
Type Table
Add Alerts to Seq#
Add the Mail App to Seq#
Click Settings, then Apps, then Install From Nuget.
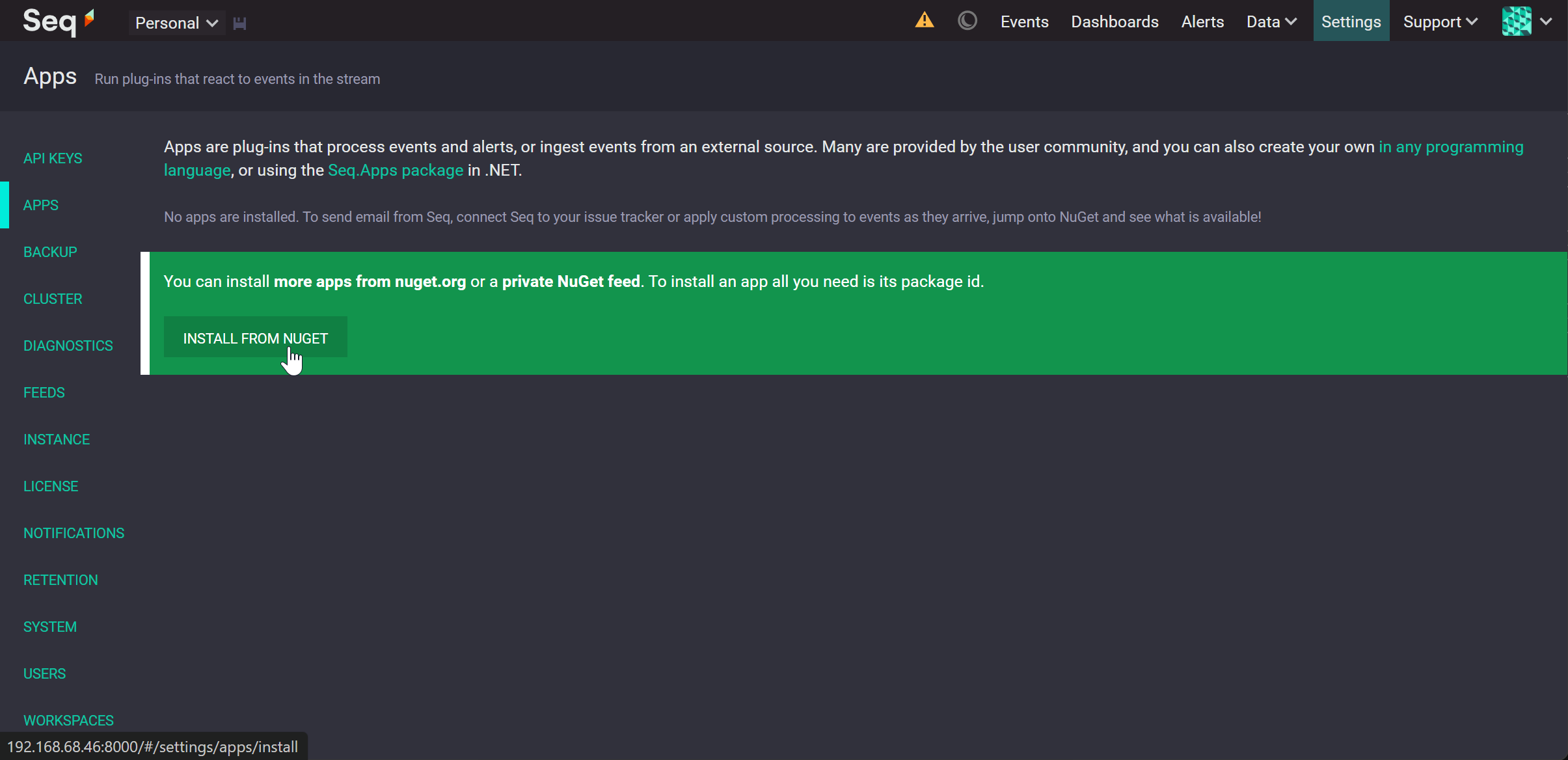
Enter Package id Seq.App.Email and click Install.
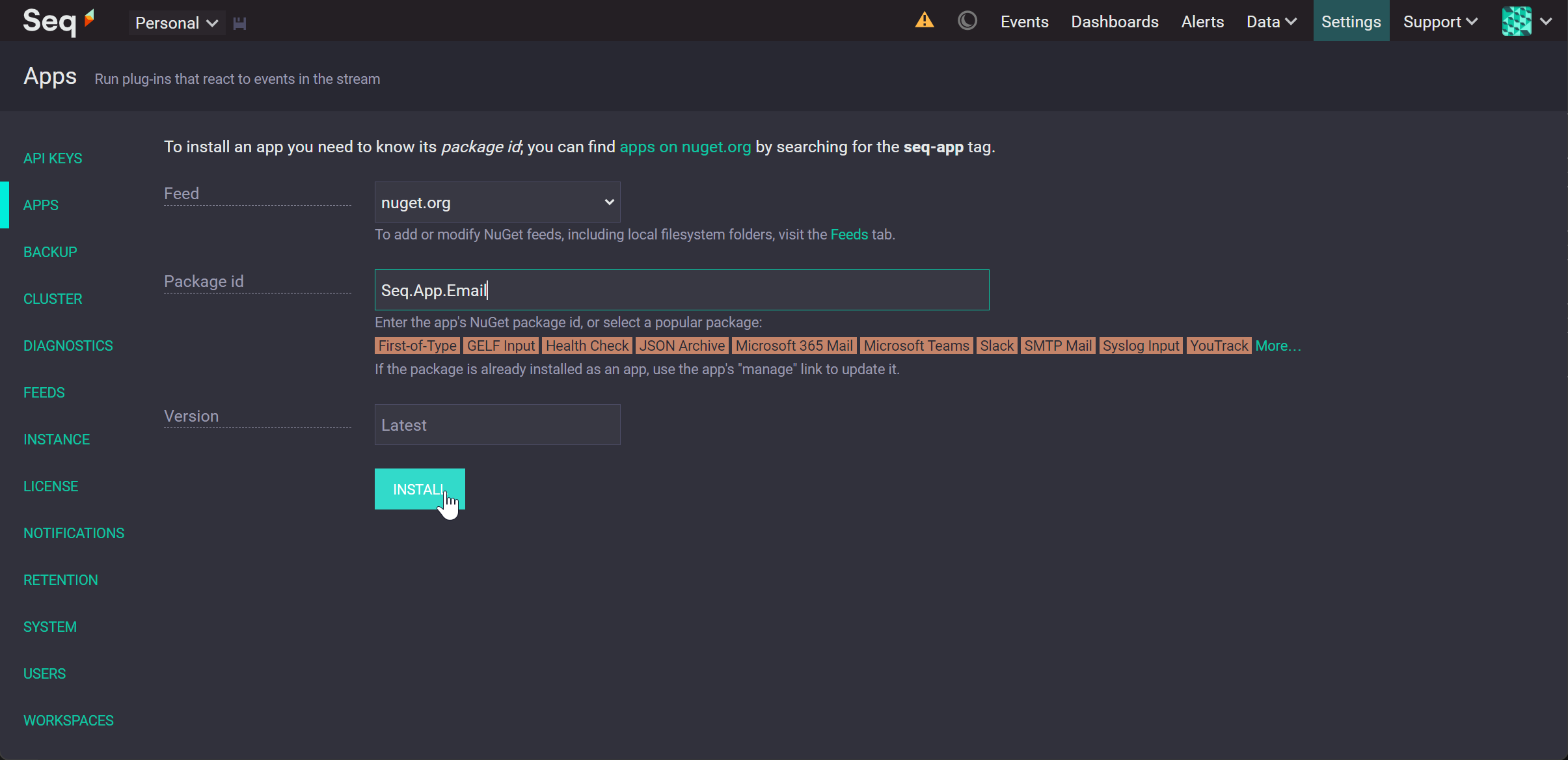
Add an Instance of the Mail App and Configure it#
Click Add Instance for the newly installed app.
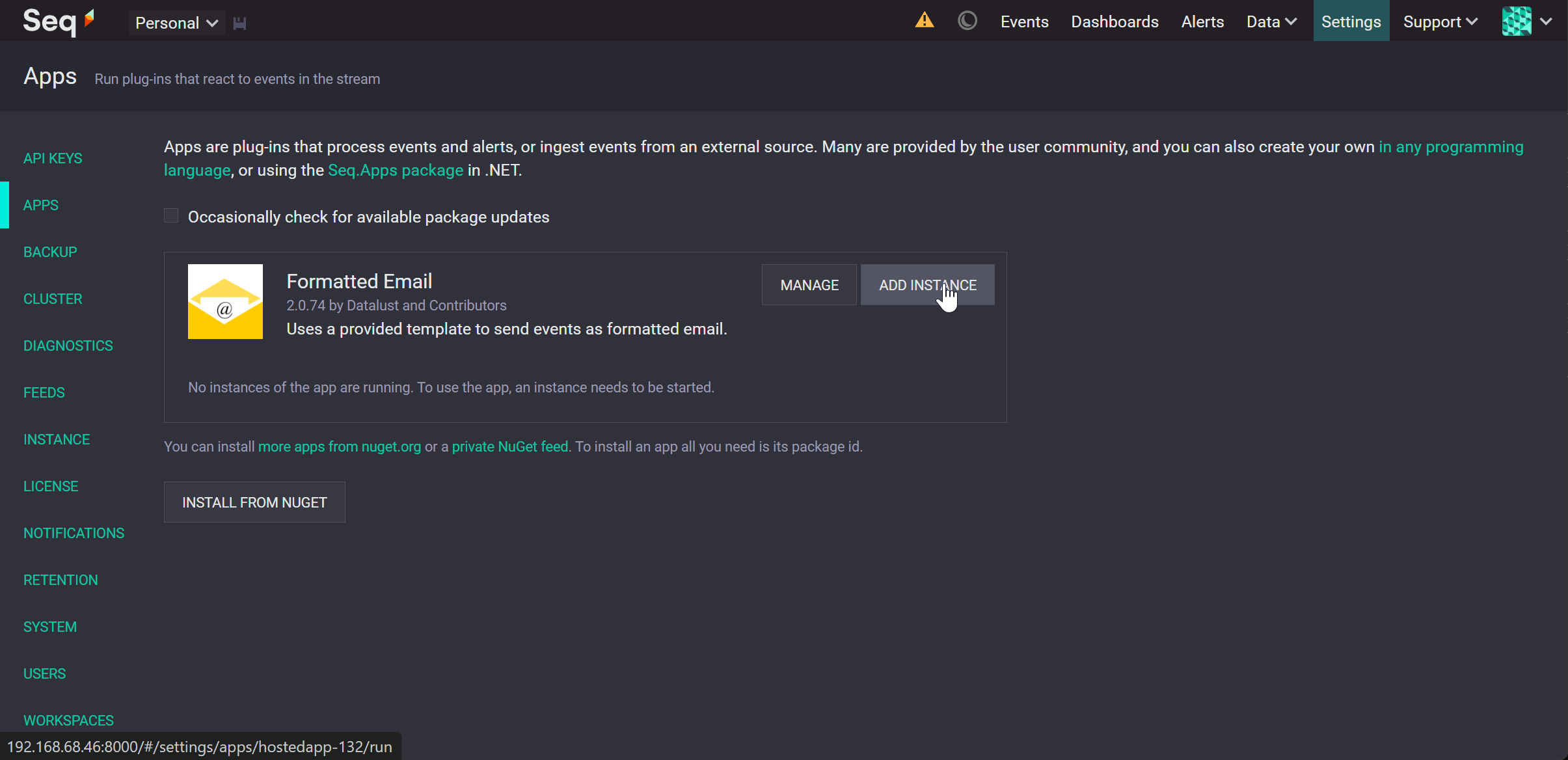
Configure the instance with the SMTP email account details.
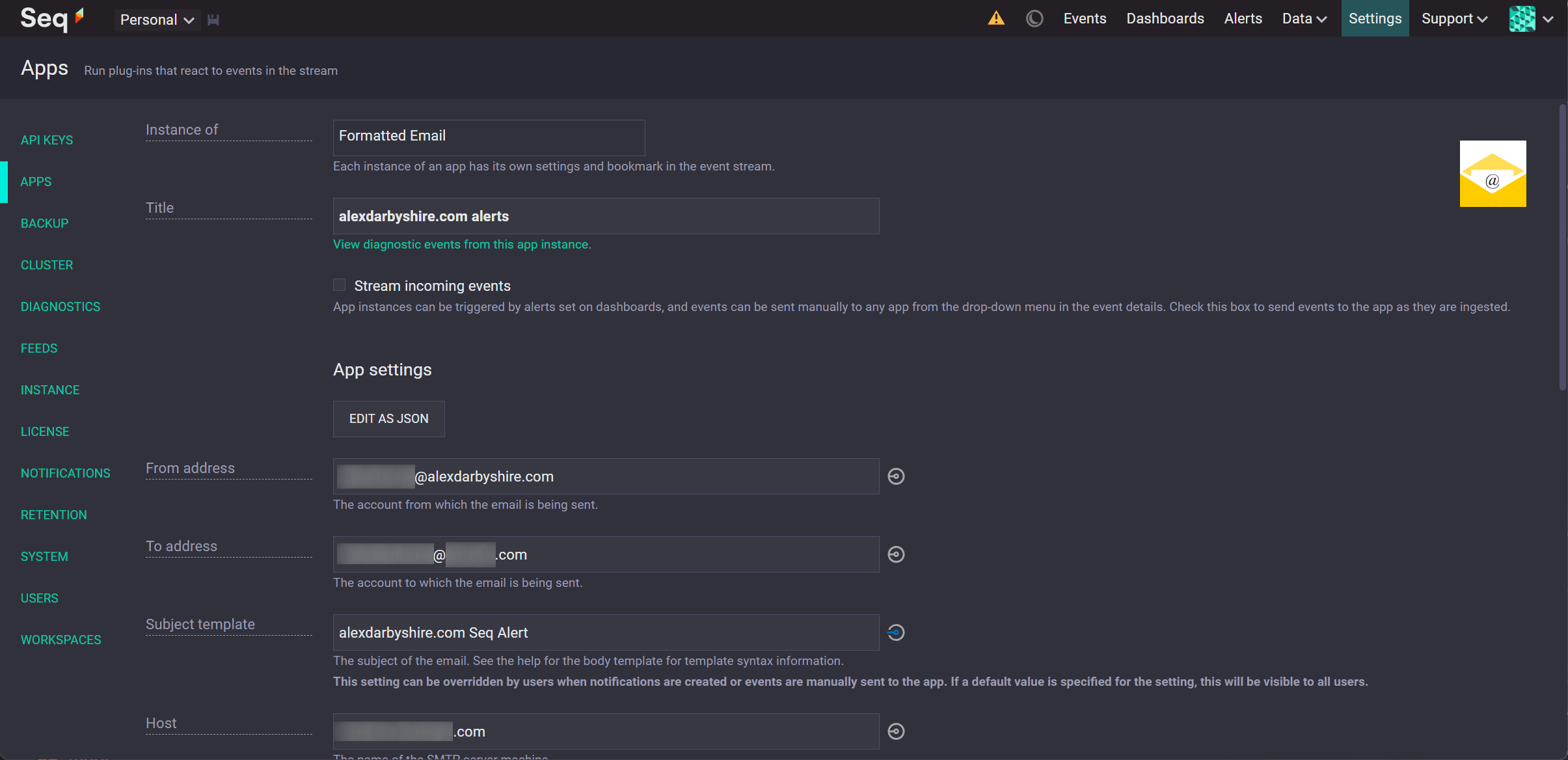
Add an Alert#
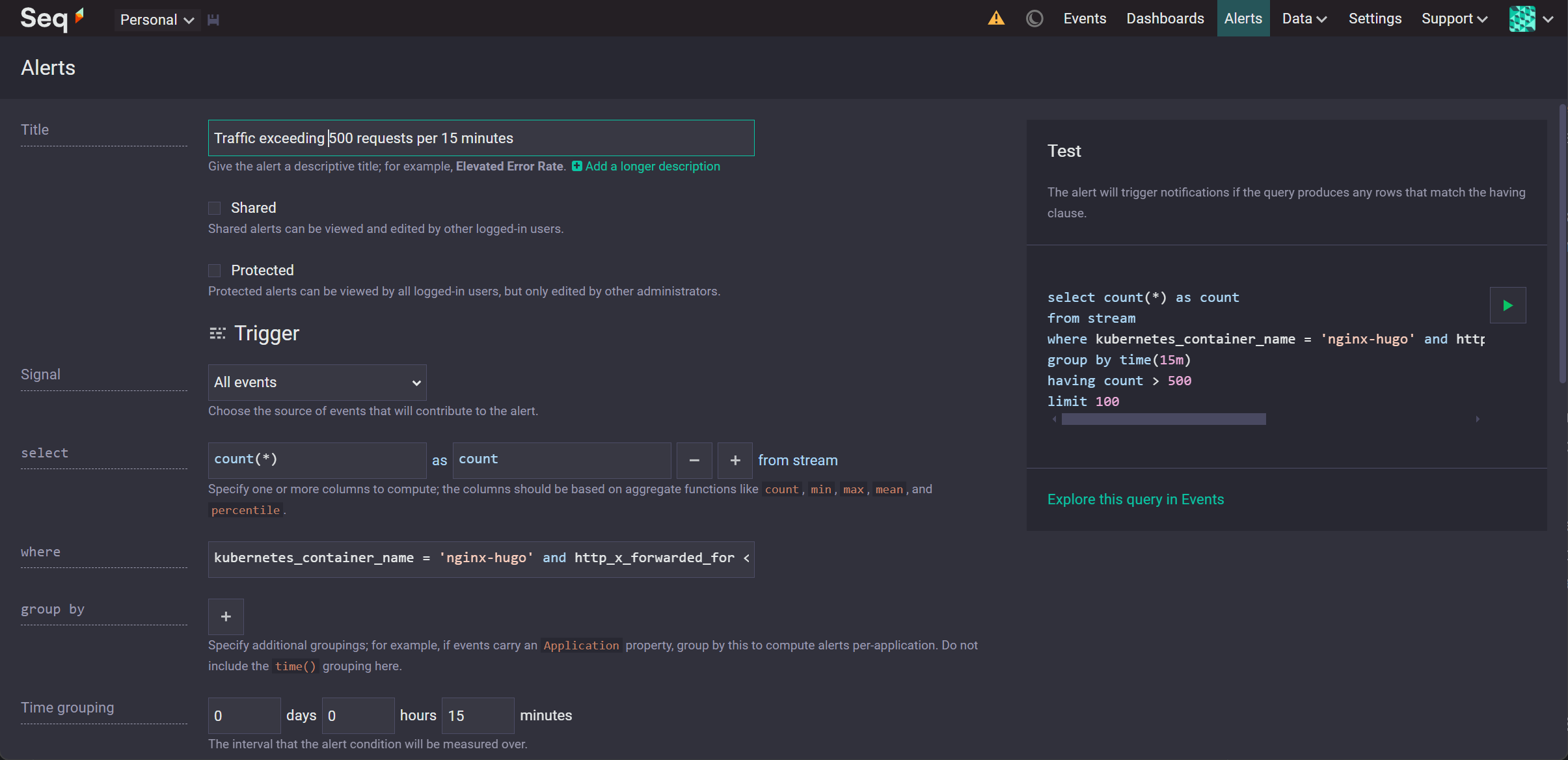
Add an alert for a query, in this example the alert is sent when there is more than 500 requests responded to with HTTP status code 200 within a 15-minute period.
Success#